Wallets
Network-Native Assets & Tokens
CoKeeps wallets can securely store both network-native assets and tokens. Both are digital assets with economic value and can be used as a medium of exchange, but they differ in how they are created, managed, and used on the blockchain.
Network-native assets (often called "native coins" or "native tokens") are issued directly by the blockchain protocol itself, typically as part of its consensus and incentive mechanism (for example, through mining or staking rewards). They exist on their own dedicated blockchain and are usually required to pay transaction fees and participate in network operations.
Tokens, on the other hand, are created ("minted") by smart contracts or programs deployed on an existing blockchain. They do not have their own blockchain; instead, they operate within the framework of a host network (such as Ethereum, Avalanche, or Tron) via smart contracts or token programs. Tokens can represent many things - fungible assets (like stablecoins), non-fungible assets (NFTs), or rights and entitlements such as ownership or access.
A single token type may exist on multiple blockchains through separate contract deployments. For example, USDT as an ERC-20 token is available on Ethereum, Avalanche, and Tron. However, these are distinct instances on each network and cannot be transferred directly between blockchains without a dedicated bridging or swapping mechanism.
NOTE
Tokens are governed by smart contracts and generally require a balance of the network-native asset to pay transaction fees. For example, when transferring USDT on the Ethereum blockchain, you must hold ETH to cover the gas fees for that transaction.
We are continuously expanding support for new networks to the best of our ability. Below is the current list of assets that you can use with both single- and multi-signature accounts:
- Arbitrum (Coming Soon)
- Bitcoin
- Bitcoin Cash (Coming Soon)
- BNB Chain
- Doge (Coming Soon)
- Ethereum
- Hedera (Coming Soon)
- Litecoin
- Maschain
- Optimism
- Polygon
- Ripple
- Solana
- Stellar*
- Tron
- World Chain
- Zetrix
Additionally, our wallet supports all ERC-20 tokens on EVM-compatible networks and SPL tokens on Solana, such as:
- Aave
- CurveDAO
- Chainlink
- MakerDAO
- Synthetix
- Uniswap
- USDT
- USDC
- The list goes on..
Networks
During testing or staging, you can use network-native assets and tokens on a blockchain's testnet or devnet. These environments are designed for experimentation and do not carry real economic value. The mainnet represents real value and is where official, production transactions are executed.
How you acquire assets depends on the network. Testnet or devnet network-native assets are often available for free from online faucet services, while mainnet network-native assets and tokens typically need to be purchased (for example, from an exchange or an individual) and then transferred to your single- or multi-signature account address.
If you require assets on test networks, we can help you source them from publicly available faucets where possible. For mainnet assets, we can assist in facilitating acquisition through our exchange partners or, where appropriate, via decentralised exchange routes, and ensure they are delivered to your designated single- or multi-signature accounts.
Smart Contracts
You can create your own tokens using CoKeeps Wallet and deploy them on any supported blockchain that provides smart contract or program capabilities.
You can also import existing smart contracts or programs from supported blockchains and interact with them directly using your single- or multi-signature accounts. For example, if the contract represents a decentralised exchange (DEX), you can call its methods and perform actions such as swapping tokens.
When you assign a CoKeeps multi-signature account to a smart contract's administrative role address, the contract automatically benefits from a governance-oriented, maker-checker structure. Administrative actions such as minting additional tokens or updating configuration will then require multiple approvals according to the multi-signature threshold, instead of being controlled by a single address.
Tokenisation
All supported token standards (such as ERC-20 and SPL) that are created or imported via CoKeeps Wallet automatically become transferable assets within the wallet, similar to other supported assets such as BTC, ETH, or USDT. You can create single- or multi-signature accounts that hold these tokens directly, and perform transfers without needing to implement custom interactions with the underlying token smart contract.
If you need to perform airdrops or a large number of transfers, we recommend using our Batch Transfers capability, which is designed to optimise operational efficiency and reduce overall transaction costs for bulk transfers.
Private Keys
CoKeeps Wallet is designed for managing structured organisational digital assets rather than for individual retail use. It serves as a tool to help you manage the private keys that control your assets. CoKeeps Cold Wallet neither controls nor stores your private keys on your behalf. The accounts you create therefore remain under the control of you and your organisation.
When a transaction requires a signature, the device running the CoKeeps Cold Wallet is responsible for generating or reconstructing the private key material locally and signing the transaction. This deterministic process is unique to your setup and uses high-entropy inputs provided during onboarding and operation. Once the signing operation is complete, the key material is immediately cleared from memory. It is not written to disk and never transmitted over the network.
Because your device plays a critical role in key generation and signing, it is essential to securely store the recovery shards produced during the initial CoKeeps Cold Wallet onboarding. To support recovery in the event of device loss or signer unavailability, the recovery secret is divided into three shards: one is stored (encrypted) by the CoKeeps Wallet system, one is held by the designated signer (the user operating the Cold Wallet), and one is held by your organisation (for example, a trusted security or infosec owner). This setup ensures that, if a signer is unavailable, access to that signer’s accounts can still be recovered. For multi-signature accounts, the impact of a single signer’s absence is naturally reduced by the multi-signature threshold, which is designed to tolerate the loss of one or more signers while maintaining control.
IMPORTANT
Endpoint security is critical. Unless your signers are extremely disciplined about what they install and how they use their devices, we strongly recommend providing dedicated, hardened devices (for example, laptops, PCs, or tablets) solely for CoKeeps Cold Wallet operations. Be especially cautious of malware such as keyloggers and screen-capture tools, which can compromise credentials and sensitive actions performed on the device. Windows users should also be aware that Microsoft has a built-in keylogger in its Operating System, and are entirely at your own risk. Your organisation is responsible for securing these devices and managing the associated operational risk.
Accounts
In the CoKeeps Cold Wallet platform, single-signature accounts are referred to as "Personal" accounts, while multi-signature accounts are referred to as "Shared" accounts.
A custodial account is a multi-signature account that includes at least one CoKeeps signer among its members. In certain scenarios such as with the Hot Wallet, a CoKeeps signer may be represented by a machine signer. Depending on your use case and configuration, a multi-signature account can include signers from both the Cold Wallet and the Hot Wallet.
There are three types of accounts:
Managed Self Custody
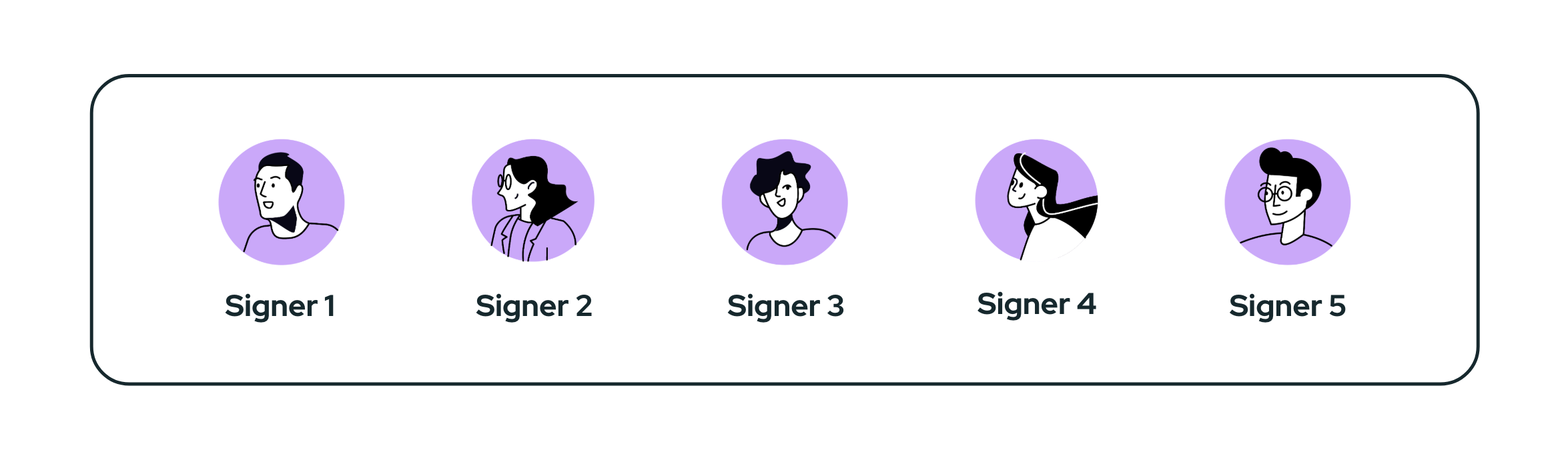
These include single- and multi-signature accounts created within CoKeeps Wallet. Multi-signature accounts under this model may consist solely of signers from your own organisation or a combination of signers from different organisations, some of whom may not be using CoKeeps Wallet to manage their accounts.
Partial Custody
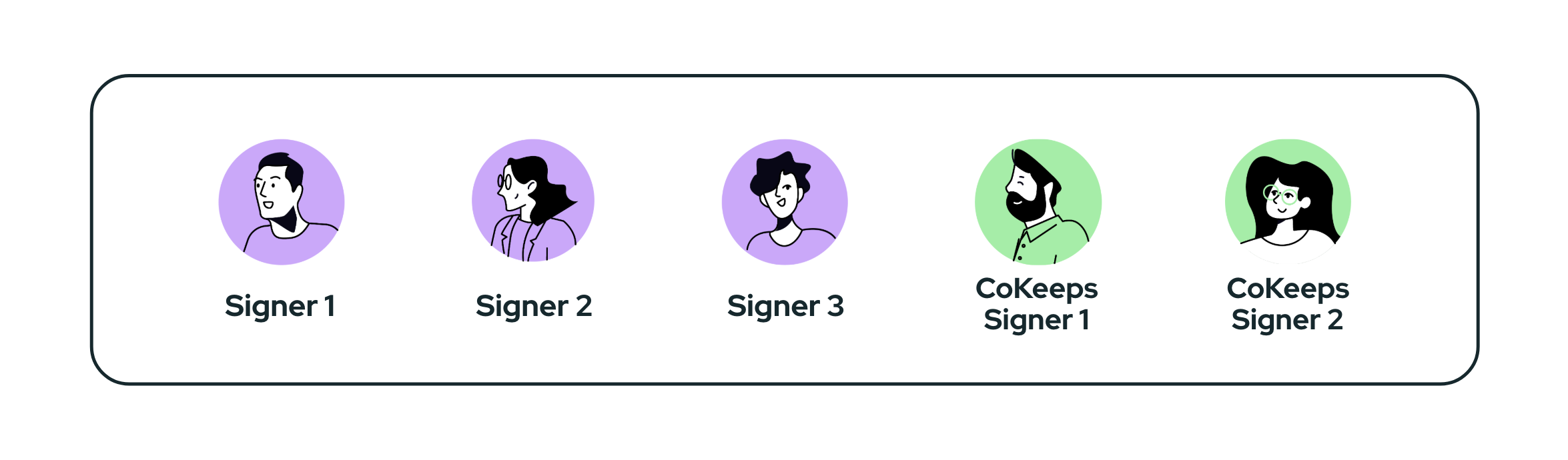
These are multi-signature accounts that include CoKeeps signers, where CoKeeps signers form the minority of the account members. This model is typically used when CoKeeps is involved primarily for recovery or contingency purposes rather than day-to-day transaction approval.
Full Custody
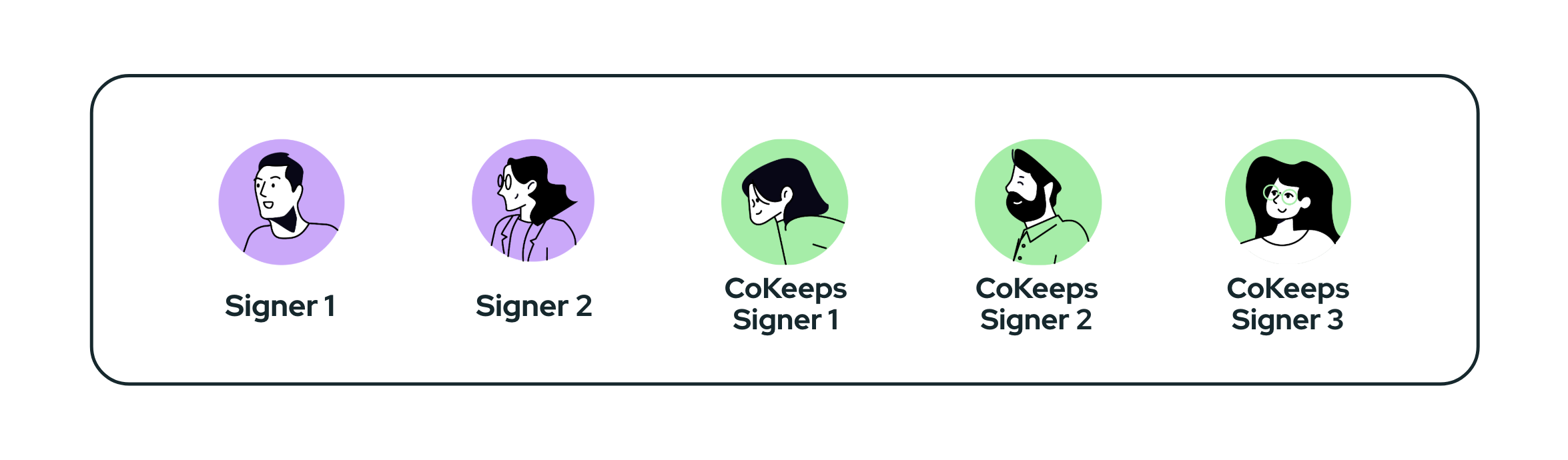
These are multi-signature accounts that include CoKeeps signers, where CoKeeps signers form the majority of the account members. This model is commonly used when regulatory or compliance requirements mandate CoKeeps' active involvement in overseeing transaction details and enforcing policy requirements.
Special Accounts
Most Special Accounts are created through Hot Wallet modules and use an MPC-based key management model, rather than the on-device key generation strategy used by the Cold Wallet. Instructions for creating these accounts are provided in the Hot Wallet section. These accounts are generally not accessible to Signers via the Cold Wallet; instead, they are managed by signer and admin roles integrating with the CoKeeps SDK (CKSDK).
These specialised roles allow you to design operational flows and governance models that match your organisation’s risk appetite and process requirements.
Deposit
Deposit accounts are designated receiving addresses for your end users. They act as temporary placeholders to identify which deposits belong to which users. Their primary purpose is to detect and attribute incoming transfers of specific assets to the correct user. Each deposit address is unique per user.
Balances in deposit accounts are not intended to be held long term. Funds should be periodically swept into a Holding or other designated account.
NOTE
For Ethereum and other EVM-compatible blockchains, CoKeeps provides a smart contract that can automatically forward incoming transfers. This removes the need for manual sweeping from deposit addresses into another account.
Holding
A Holding account is a multi-signature account created via CoKeeps Cold Wallet and is dedicated to storing funds swept from deposit addresses, or used as an omnibus structure. An omnibus account is a single on-chain account holding specific assets on behalf of many virtual user balances tracked in an off-chain ledger.
Typically, a minority portion of the balance in a Holding account is periodically transferred to Withdrawal accounts. This allows end-user withdrawals to be processed quickly, as transactions from a Holding account usually require human participation (e.g., multi-signature approval), which can introduce operational delay.
Withdrawal
The sole purpose of a Withdrawal account is to enable fast transfers from your organisation's held assets to the destination addresses specified by your end users. These accounts are typically funded from Holding or Deposit accounts to support timely, automated payout flows.
Signer
A Signer account is a single-signature account derived from a label. Even when the same label value is used, the resulting Signer account is unique per user. The address of a Signer account can be used in multiple ways, such as:
- Acting as a member of a multi-signature account, participating primarily during recovery procedures, automated approvals, or approvals initiated via your own platform;
- Serving as a lightweight omnibus account (with fewer controls and therefore lower security assurances compared to a dedicated Holding account); or
- Functioning as an individual wallet account for each CKSDK user, allowing them to perform standard wallet operations - including transfers and smart contract interactions - in a manner similar to browser wallets such as MetaMask.
Gas Station
In blockchain networks that use smart contracts, gas fees (paid in the network-native asset) are required for executing transactions - whether they involve the native asset itself or tokens. These fees are normally deducted from the account that initiates the transaction, which can create operational friction if each account must maintain its own gas balance.
The Gas Station feature in CoKeeps automates this process by ensuring that designated accounts always have sufficient network-native assets available to cover gas fees.
On the CoKeeps platform, all transfers except internal movements within an omnibus structure are executed on-chain and therefore require gas. For example, when user A transfers funds to user B using their Signer accounts, the transaction is broadcast to the network and consumes gas.
The Gas Station uses an auto-funding mechanism:
- CoKeeps continuously monitors configured accounts for incoming and outgoing events and checks their gas balances.
- When a balance falls below a predefined threshold, the Gas Station automatically initiates a top-up transfer from a designated funding account, according to the parameters you have configured (e.g., minimum balance, refill amount, source account).
This ensures that end-user and operational accounts can continue to transact without manual intervention to maintain gas balances.
NOTE
Gas Station parameters and funding sources are configured via the CoKeeps Client Administration platform.
Risk Management
Multi-signatures
Accounts that require more than one signature are inherently more secure than single-signature accounts. Using Shamir Secret Sharing on a single private key as used by some wallet is not a replacement for a true multi-signature account. Wherever possible, prioritise multi-signature accounts over single-signature accounts.
Distribution
Avoid concentrating all assets in a single account. Distribute holdings across multiple multi-signature accounts with different owners and, where appropriate, different roles and scopes. This limits the impact of any single account or key being compromised.
Higher Threshold
Choose more resilient thresholds wherever operationally feasible. For example, a 3-of-5 multi-signature configuration is more robust than a 2-of-3: it can tolerate the loss or unavailability of two owners simultaneously, and the additional required signature further reduces the risk of collusion or compromise.
Custodian
CoKeeps operates as a regulated entity under the oversight of the Securities Commission Malaysia. Our responsibilities extend beyond safeguarding your digital assets to adhering to established security, governance, and policy requirements applicable to licensed custodians.
